Diabetic Neuropathy
The diabetic neuropathy is an affectation of the secondary autonomous and peripheral nervous system to diabetes. In this way, it consists of the loss of the regenerative capacity of the nerve fibers due to the joint action of metabolic and vascular factors. Next, we will detail what it consists of, its symptoms and treatment.
Types of neuropathy
The cynical manifestations vary according to the area of the nervous system that is affected. Therefore, they can be distinguished:
1. Distal symmetric motor-sensory polyneuropathy
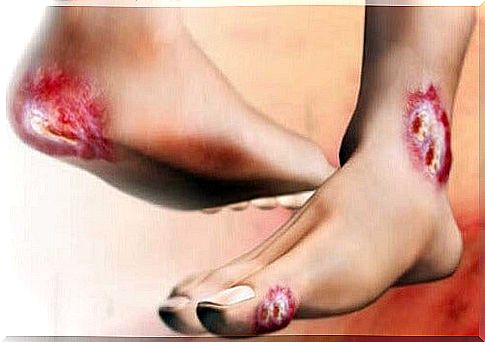
This is the most prevalent neuropathy. First, the symptoms reported by patients are pain and hyperalgesia (excessive sensitivity to pain). This is followed by the degeneration of the axons of the sensory neurons. So desensitization is caused in the process of thermoreception and distal pain.
The manifestations appear earlier in the lower limbs and later in the upper ones. In addition, desensitization causes ulcerative symptoms on the feet that often degenerate into gangrene. Sometimes the only way to treat it is amputation. Otherwise the patient is exposed to sepsis.
2. Focal mononeuropathy
It affects the cranial nerves III, IV and VI. Which is evidenced by the presence of abnormalities in the pupillary reflexes. In addition to a possible one-sided pain.
3. Polyradiculopathy
Proximal motor radiculopathy affecting the lumbar spinal cord roots (L2, L3 and L4). It is accompanied by atrophy and pain in the muscles of the thigh and pelvis. It has a higher incidence in men over 65 years of age. This sector of the population is more susceptible to suffering from diabetic neuropathic cachexia, due to:
- Weight loss.
- A possible depression.
- Poor glycemic control.
4. Autonomic neuropathy
This is more complex than the previous ones and ends up affecting different organs, although in its early stages it may go unnoticed. For this reason, its symptoms are more general and diffuse.
How does diabetic neuropathy occur?
As we saw at the beginning, it is the sum of the metabolic and vascular components that causes this affectation:
1. Metabolic factors
Hyperglycemia causes the appearance and storage of glycosylated compounds and sorbitol, as well as increased oxidative stress. In fact, at the neuronal level, sorbitol modifies cellular metabolism and lowers the concentration of compounds that promote neuronal regeneration, such as myoinositol.
2. Vascular factors
The above situation increases the permeability of the vessels and blood coagulation. Therefore, added to small microangiopathies of the capillaries that vascularize the nerve, they cause diabetic neuropathy.
Diagnosis and prevention of diabetic neuropathy
The diagnosis is made based on the clinical history of the patient (who must have been previously diagnosed as diabetic). Once the history has been evaluated, we proceed with an assessment of the neuropathic symptoms and, finally, a physical examination of the feet and other sensitivity tests (pain, temperature, sensation, among others) will be performed.
Regarding prevention measures, it is especially important to maintain glycemic control to try to avoid as many complications as possible and maintain the well-being of the patient. In addition, this must be accompanied by care for other triggers such as hypertension, obesity, tobacco, and alcohol.
Treatment of diabetic neuropathy
In general lines, to establish the treatment of diabetic neuropathy we must differentiate between one or another etiology:
1. Treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
It is essential to keep blood glucose peaks under control. Especially in the cases of patients in which it has already been triggered. In addition, this measure must be supported by daily foot care, in order to prevent any situation that could lead to ulcer and amputation due to gangrene. In this sense, the use of suitable footwear and personal hygiene are especially important.
Neuropathic pain will manifest itself in both feet and this can be combated by walking. On a pharmacological level, it is fought with tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline (Tryptizol), which is the drug of choice.
2. Treatment of autonomic diabetic neuropathy
In this case, the affectation is multi-organ, so the treatment is focused on alleviating the local symptoms of the affected area:
- Orthostatic hypotension. Drop in tension when getting up from a horizontal position. This symptom can be combated with fludrocortisone acetate, the side effect of which can be high blood pressure.
- Diabetic gastroparesis. Difficulty proceeding with gastric emptying. It is advisable to practice frequent and light food intakes. On a pharmacological level, the drug of choice is metoclopramide and domperidone, marketed as Primperan and Motilium respectively.
- Enteropathy. By reducing the motility of the small intestine, fluid absorption is reduced and bacterial proliferation is stimulated. This causes diarrhea interrupted by the counterpart, constipation due to the alteration of the large intestine. In the most extreme cases, the rectum is affected and the patient has fecal incontinence.
- Erectile dysfunction. It can be solved by stopping treatment with hypotensive drugs. If there is a contraindication, treatment with phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors is recommended in order to facilitate vasodilation and the corpora cavernosa. The best known drug is sildenafil, which is sold under the name Viagra. In the event that the pharmacological treatment is ineffective, a penile prosthesis (surgical process) can be used.
- Hyperhidrosis in the head and trunk. It is treated with drugs whose adverse effects limit its use. Excessive gustatory sweating is treated with botulinum toxin.
Diabetic neuropathy: final comments
In summary, prompt treatment of diabetic neuropathy by the specialist is essential . It is recommended to follow the medical treatment rigorously. Fortunately, nowadays, there are better and less aggressive treatments. Therefore, today there is more hope for these patients.