Symptoms Of Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease is not really a disease, but rather a term that is used to describe the normal changes that occur in the vertebral discs as we age. The vertebral discs act as shock absorbers for the spine, allowing it to bend and rotate.
When degenerative disc disease occurs, the passage openings of the nerves in the spine narrow and do not cushion impacts, especially when running or jumping. On the other hand , most of the time it occurs in the discs of the lumbar and cervical area.
What Causes Degenerative Disc Disease?

As we age, the spinal discs deteriorate, which can lead to degenerative disc disease in some people. Some of the changes due to age are:
- Loss of fluid in the discs: This causes the discs to lose their ability to act as shock absorbers. Likewise, the thickness of the disc and the distance between the vertebrae also decrease.
- Cracks in the outer layer of the disc: resulting in the gelatinous material of the disc that can come out and cause the disc to rupture.
These changes are more likely to be suffered by people who are smokers, obese and who do heavy physical work. Similarly, wear and tear, incorrect posture, and incorrect body movements can also weaken the disc and cause degeneration.
Symptoms of degenerative disc disease
This disease can cause neck or back pain, depending on the location of the damaged discs. However, if the affected disc is in the neck, it can cause neck or arm pain. Meanwhile, if the affected disc is in the back, pain may appear in the back, buttock or legs.
The pain is often worse with movements such as bending, stretching, or twisting. It can also appear after an injury, even after performing a normal movement such as bending over to lift an object. In other cases, you may feel tingling and numbness in one leg or arm.
Disc degeneration is actually a natural part of aging, and over time, all people will have changes in their discs depending on the degree of wear and tear.
However, not everyone will develop symptoms. In fact, degenerative disc disease is quite variable in nature and severity.
Diagnosis of degenerative disc disease
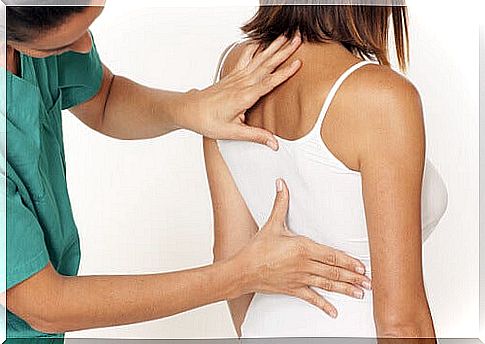
This disease is diagnosed through a physical exam and questions about symptoms, injuries, illnesses, habits, and activities you do. In the physical examination, the doctor assesses the range of motion of the affected area and whether there is pain due to movement.
The specialist will also look for areas of tenderness and nerve-related changes such as tingling, numbness, or weakness in the affected area. In turn, it will check for other conditions such as fractures, tumors, and infections.
The imaging is used when:
- Symptoms after injury.
- Suspicion of nerve damage.
- Other conditions that can affect the spine.
How is it treated?
To relieve pain, you can apply cold or heat as you feel better in the affected area. Also, the doctor will prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen or naproxen. If necessary, the doctor can recommend stronger medications.
Drug treatment can be complemented with physical therapy and exercises to strengthen and stretch the back. In some cases, surgery may be required. Surgery usually involves removing the damaged disc. However, in some cases, the bone is permanently attached to protect the spinal cord.
If the health problem consists of a herniated disc, osteoarthritis, or spinal stenosis, it will most likely require other treatments.